Tag Archive for: Security
SSL Certificate
Introduction to the types of SSL certificates that are provided by us:
1) Positive SSL
-Provides HTTPS secured link for a naked domain and it’s subdomain with “www.” (Example: abc.com and www.abc.com)
-$10,000 warranty provided by comodo.
2) Comodo SSL
-Provides HTTPS secured link for a naked domain and it’s subdomain with “www.” (Example: abc.com and www.abc.com)
– A Comodo SSL Certificate is the quickest and most cost effective way for an online business to protect customer transactions.
-$250,000 warranty provided by comodo.
3) Positive SSL Wildcard
-Provides HTTPS secured link for a naked domain and all of its subdomain. (Example: abc.com, www.abc.com, host.abc.com, domains.abc.com etc.)
-A Wildcard SSL Certificate saves you money and time by securing your domain and unlimited sub-domains on a single certificate. Wildcard certificates work the same way as a regular SSL Certificate, allowing you to secure the connection between your website and your customer’s Internet browser – with one major advantage. A single Wildcard SSL Certificate covers any and all of the sub-domains of your main domain.
-$10,000 warranty provided by comodo.
4) EV SSL
– Provides HTTPS secured link for a naked domain and it’s subdomain with “www.” (Example: abc.com and www.abc.com)
– An EV SSL certificate offers the highest available levels of trust and authentication to your website.
– The green address bar prominently displays your company name and provides highly visual assurance to customers that your site is secure – immediately giving them the confidence to complete their transaction.
– $1,750,000 warranty provided by comodo.
7 ways admins can help secure accounts against phishing in G Suite
We work hard to help protect your company against phishing attacks—from using machine learning, to tailoring our detection algorithms, to building features to spot previously unseen attacks. While we block as many external attacks as we can, we continue to build and offer features designed to empower IT administrators to develop strong internal defences phishing, Security, email security against phishing.
Here are seven things we recommend admins do in G Suite to better protect employee data.
1. Enforce 2-step verification
Two-step verification (2SV) is one of the best ways to prevent someone from accessing your account, even if they steal your password. In G Suite, admins have the ability to enforce 2-step verification. 2SV can reduce the risk of successful phishing attacks by asking employees for additional proof of identity when they sign in. This can be in the form of phone prompts, voice calls, mobile app notifications and more.

G Suite also supports user-managed security keys—easy to use hardware authenticators. Admins can choose to enforce the use of security keys to help reduce the risk of stolen credentials being used to compromise an account. The key sends an encrypted signature and works only with authorized sites. Security keys can be deployed, monitored and managed directly from within the Admin console.
Watch “The Key to working smarter faster and safer” on YouTube
2. Deploy Password Alert extension for Chrome
The Password Alert chrome extension checks each page that users visit to see if that page is impersonating Google’s sign-in page and notifies admins if users enter their G Suite credentials anywhere other than the Google sign-in page.
Admins can enforce deployment of the Password Alert Chrome extension from the Google Admin console (Device management > App Management > Password Alert)—just sign in and get started. You should check “Force installation” under both “User Settings” and “Public session settings.”
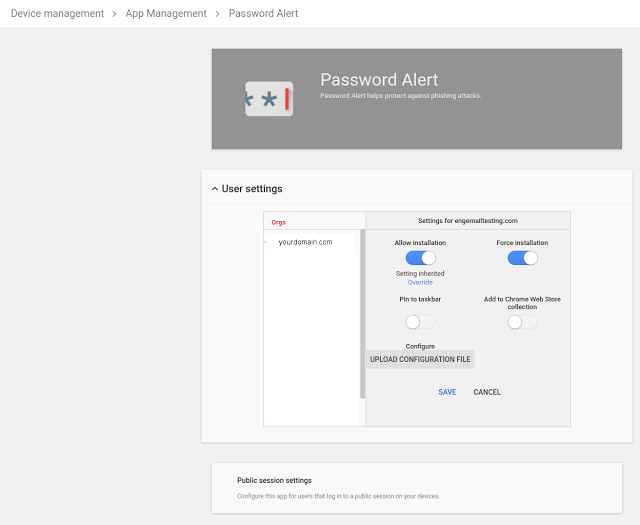
Admins can also enable password alert auditing, send email alerts and enforce a password change policy when G Suite credentials have been used on a non-trusted website such as a phishing site.
3. Allow only trusted apps to access your data
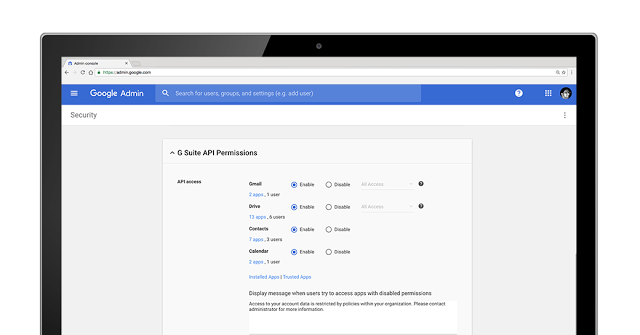
Take advantage of OAuth apps whitelisting to specify which apps can access your users’ G Suite data. With this setting, users can grant access to their G Suite apps’ data only to whitelisted apps. This prevents malicious apps from tricking users into accidentally granting unauthorized access. Apps can be whitelisted by admins in the Admin console under G Suite API Permissions.
To help your business avoid damage to its reputation from phishing attacks and impersonators, G Suite follows the DMARC standard. DMARC empowers domain owners to decide how Gmail and other participating email providers handle unauthenticated emails coming from your domain. By defining a policy and turning on DKIM email signing, you can ensure that emails that claim to be from your organization, are actually from you.5. Disable POP and IMAP access for those who don’t need it
The Gmail clients (Android, iOS, Web) leverage Google Safe Browsing to incorporate anti-phishing security measures such as disabling suspicious links and attachments and displaying warnings to users to deter them from clicking on suspicious links.
By choosing to disable POP and IMAP, admins can ensure that all G Suite users will only use Gmail clients and benefit from the built-in phishing protections that they provide. POP and IMAP access can be disabled by admins at the organizational unit level.
Note: all third-party email clients including native mobile mail clients will stop working if POP and IMAP are disabled.

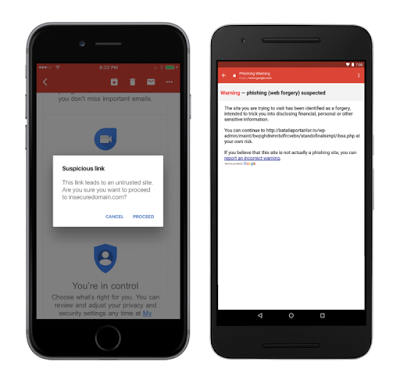
By default, Gmail clients (Android, Web) warn G Suite users if they’re responding to emails sent from outside their domain by someone they don’t regularly interact with, or from someone not in their contacts. This helps businesses protect against forged emails, from malicious actors or just plain old user-error like sending an email to the wrong contact. Educate your employees to look for these warnings and be careful before responding to unrecognized senders. Unintended external reply warnings are controlled by the Admin console control in the “Advanced Gmail” setting.
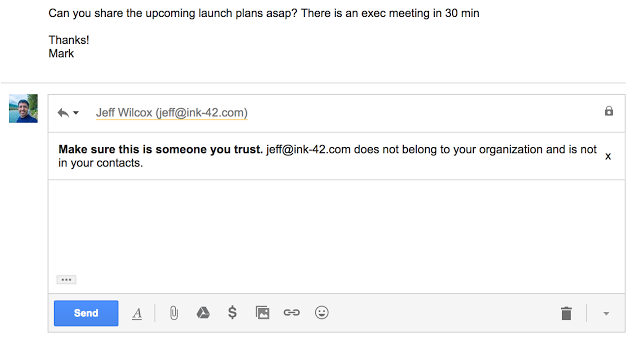
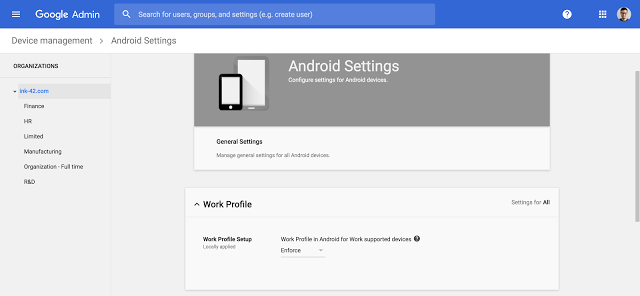
Work profiles allow you to separate your organization’s apps from personal apps, keeping personal and corporate data separate. By using integrated device management within G Suite to enforce the use of work profiles, you can whitelist applications that access corporate data and block installation of apps from unknown sources. You now have complete control over which apps have access to your corporate data.
Reference by Google.com
Beware of Spora – a professionally designed ransomware
Spora is a recent addition to the ransomware family that Quick Heal Lab has come across. It is a file encryptor ransomware that encrypts a user’s files with strong encryption algorithm and demands a ransom. Spora is launched with a good infection routine, the capability to work offline, well-designed and managed payment portal dashboard, decryption key purchase options.
Infection Vector
Spora is delivered to the victim via spam emails containing a malicious .ZIP file as an attachment. This .ZIP file contains an HTML Application (‘.HTA’) file that pretends to be an invoice in .PDF or .DOC format, wearing double extensions to those files (e.g. <file_name>.pdf.HTA). As ‘Hide extensions for known file types’ option is marked checked by default in many systems, it increases the chances of getting trapped in opening an .HTA file by mistaking it for harmless file types.
Infection Routine
Spora has a multistage infection behavior. When a malicious .HTA file is executed, it drops and executes the below files into the system using VBScript program:
- ‘%Temp%\close.js’
- ‘%Temp%\doc_6d518e.docx’
• It is actually a file encryptor component that performs file encryption.
• doc_6d518e.docx is a corrupt file that is intentionally dropped and opened to keep the victim busy in viewing it while files are getting encrypted in the background.
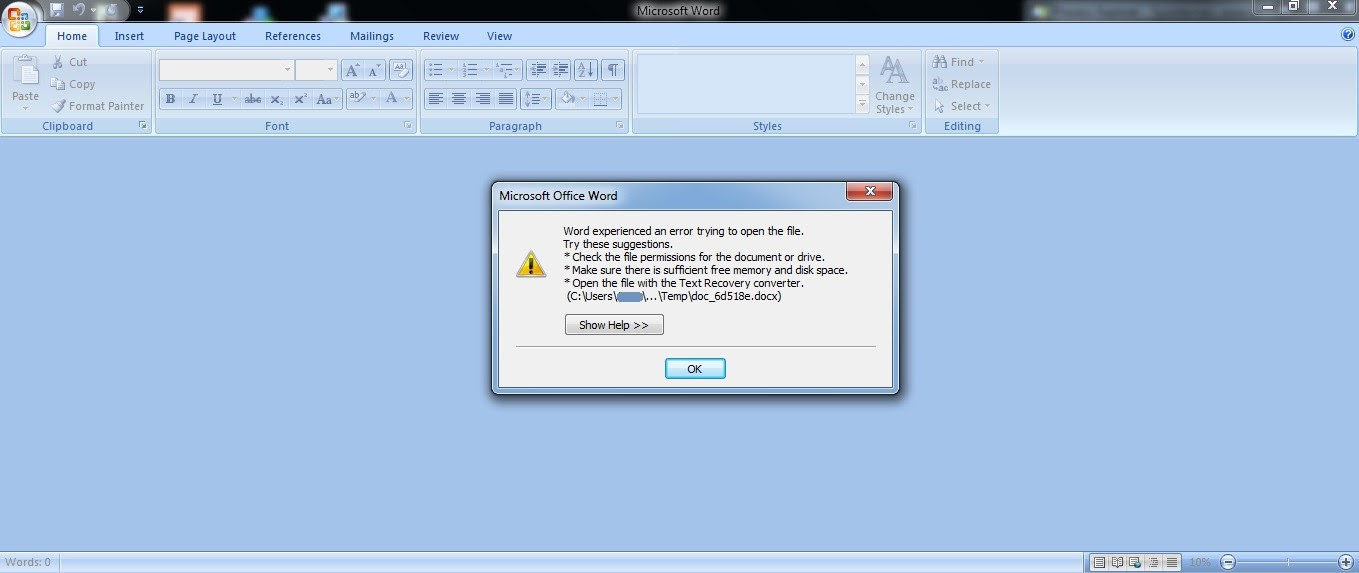
Figure 1: Corrupt document to fool a victim
Spora was not found appending any extension to the encrypted files. When encryption is over, a ransom note is displayed (shown below), highlighting the uniquely generated ‘Infection ID’ and basic instructions.
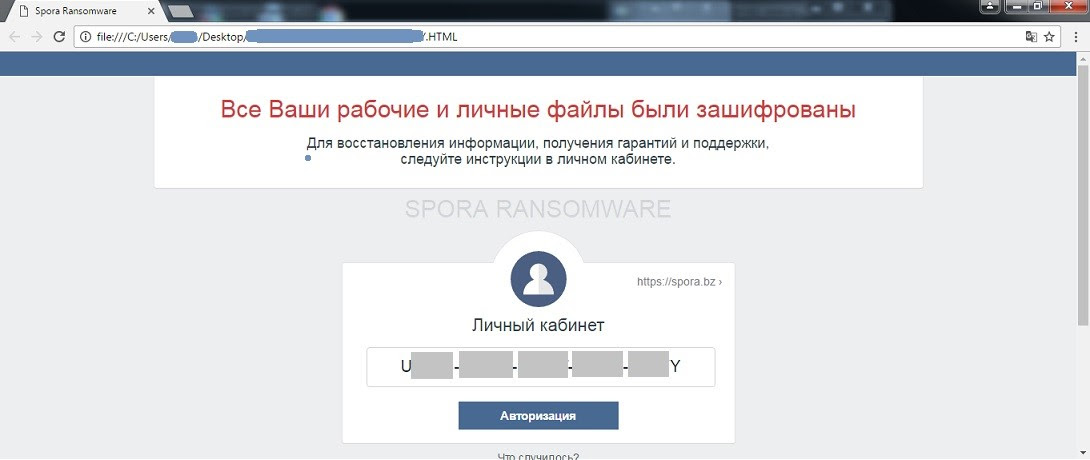
Figure 2. Spora ransom note with an infection ID
A .KEY file is dropped on the desktop, containing information about ‘encrypted-encryption keys’ used to encrypt files. In order for the victim to get complete access to the payment portal, they need to upload .KEY file to the portal to synchronize the infected computer with the payment portal. To do so, the below panel is provided.
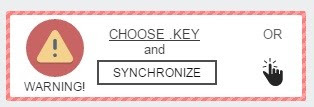
Figure 3. Key upload panel on Spora payment portal
Once synchronized, the victim can choose from a number of purchase options available on a ‘My Purchase’ section of the portal.
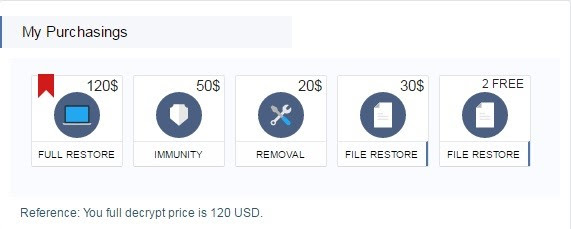
Figure 4. Decryptor purchase options
FULL RESTORE – With this, the user can have all their encrypted data restored.
IMMUNITY – With this, the user can buy immunity against future Spora attacks.
REMOVAL – With this, the user can have the Spora malware completely removed from their computer.
FILE RESTORE – Offers two options; decrypt two files for free or decrypt a selection of files for $30.
As you can see, Spora offers the victim with a variety of options to take care of the situation. For instance, a victim might be less likely to pay the ransom because they know they have safely backed up their data. However, they would still want to have the malware removed from the system – which gives the ‘Removal’ option.
Quick Heal Detection
Quick Heal antivirus successfully prevents Spora infections at multiple stages.
• Quick Heal Email Protection successfully prevents download of the malicious .ZIP attachment which is the first stage of the infection.
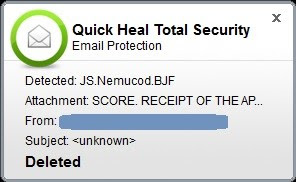
Figure 5. Quick Heal Email Protection
As shown in the image above, the malicious .HTA file has been successfully detected as ‘JS.Nemucod.BJF’ and deleted thereafter.
• Quick Heal Anti-ransomware protection successfully detects potential file encryption activities and alerts the user
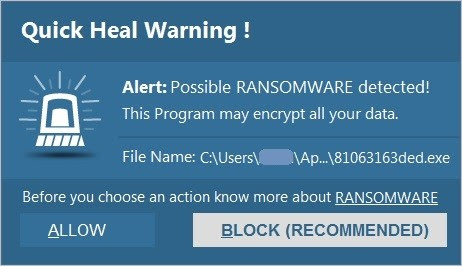
Figure 6. Quick Heal Anti-Ransomware alert
• Quick Heal Behavior Detection System successfully detects malicious activities and alerts the user
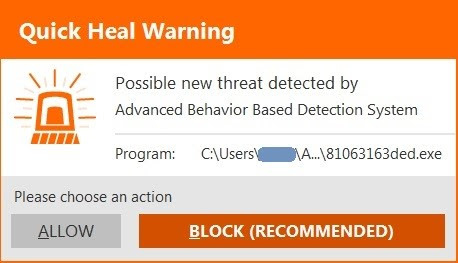
Figure 7. Quick Heal Behavior Detection System alert
Conclusion
It is not hard to guess that the creators of Spora have taken their time in developing this ransomware to make it effective, and professional at the same time.
A nicely designed decryptor portal dashboard, synchronization between the portal and infected system using a .KEY file, and multiple purchase option for decryption signify how attackers are using complex tactics in creating ransomware.
How to stay safe against such ransomware attacks
- Never download attachments that arrive in emails from unknown or unexpected sources.
- Take regular backups of your files. Remember to disconnect the Internet when you are backing up on a hard drive. Unplug the drive before you go online again.
- Apply all recommended security updates (patches) to your Operating System, and programs like Adobe, Java, web browsers, etc.
- Install an antivirus software that offers several layers of security. More importantly, keep the software up-to-date.
Reference by Quick Heal
Data Privacy Day – 10 tips to keep your data secure
Recognized annually on January 28th, Data Privacy Day is defined as a centered approach towards respecting privacy, safeguarding data, and enabling trust. It is a global effort to raise and promote awareness around protecting one’s data and privacy. With this thought in mind, we have put together these 10 security tips on Data Privacy Day.
10 Security Tips on Data Privacy Day
1. Change the passwords of your online accounts. Here are some tips to build strong and unique ones:
- Use a mix of uppercase and lower letters
- Use special characters
- Use numbers
- Use at least 8 characters
Also, here’s a fun way to create a password that is strong and can be easily remembered. First, think of a phrase or the title of your favorite book or movie; say, “The Girl With The Dragon Tatoo”. Now, take the first letter of every word in the title – this will give you tgwtdt. Capitalize a letter, add some numbers, and special characters – and you will have the ultimate password Tgwtdt#$8945B. We tested the strength of this password, and it seems that a hacker will take about 273 years to crack it. Find it out yourself – https://www-ssl.intel.com/cont
2. Take a back up of all your important data stored on your computer and mobile device. You can either take the backup over Cloud or an external hard drive. Taking regular data backups can save you from the aftermath of a virus attack or system crash – especially a ransomware infection. Ransomware is a malware that hijacks your data and demands money (ransom) to release it.
3. Data Privacy Day is not only about storing or saving data. It also advocates the importance of disposing of your information securely. Data that you delete from your computer or mobile device does not really get deleted permanently. It can still be recovered with advanced data recovery tools. So, while removing sensitive information, ensure it is gone forever. Know how to delete your data securely.
4. It is unsafe to store login ID and passwords, banking details, social security number, and other such sensitive information on your mobile device or computer. But, if you can’t help it, ensure that the data is encrypted. When you encrypt an information, it gets converted into an unreadable form, and can only be read by you. So, even if a situation arises wherein your data falls into the wrong hands, you can rest assured that it won’t get misused.
5. Just like you won’t hand over your wallet, ID card, or house key to a stranger, avoid sharing your personal information on the Internet; these could be unfamiliar websites, survey forms, online friends, unsolicited emails, and anything/anybody that asks for your information. When it comes to Data Privacy, it’s wise to be a miser in sharing your data.
6. Banking or shopping online using unsecured Wi-Fi networks can let attackers steal your personal and financial information. While using any such network, ensure it is accessible only with a login ID and password.
7. Before installing any mobile app, review its permissions carefully. Many a time, you may come across an app that asks for permissions that are not actually required for it to function on your device. For instance, if a simple Flash Light app is asking your permission to access your device’s Internet, contact details, photos, etc., then chances are it is a malicious or a potentially dangerous app. So, stay cautious against such threats.
8. One of the greatest threats to your data and privacy is phishing. Phishing is defined as an attempt to trick you into providing your personal or financial details so that the attacker can commit illegal acts using your name. Any unknown or unexpected communication (email, call, SMS, etc.) that carries a sense of urgency and requires you to provide your personal information should be treated as a phishing attack. Always ignore such communications and report them to the right authority.
9. With mobile devices becoming an integral part of our everyday lives, they store massive amounts of data about us, our friends and family members. More importantly, being smaller and compact, they are more vulnerable to theft. So, it is only logical to protect these devices with a PIN, fingerprint or a password. We do not recommend the Pattern Lock because they are easily noticeable and less secure. Also, it is wise to keep the Automatic Lock feature ON at all times.
10. While you follow all the steps mentioned above, also consider getting a trusted antivirus solution. The software that you choose must offer multiple layers of security that can block ransomware, fake, infected and phishing websites, emails designed for phishing attacks, malicious downloads, and unauthorized data storage devices.
Reference by Quick Heal










